What is it?
Thermwood's CutLayer system transforms sheet materials (composites, aluminum, wood, MDF, foam and more) into large, production-ready tooling, molds and patterns. Layers are precision-cut, aligned and bonded for exceptional strength and accuracy.
The CutLayer Process
- Design Your Part: Start with a CAD model of your tool, mold or pattern.
- Automated Nesting and Layering: The software automatically slices the design into precise layers and nests them efficiently on sheet materials.
- CNC Cutting: Each layer is cut from sheet stock (composites, aluminum, wood, MDF, foam or plastics) with CNC precision.
- Alignment and Bonding: Cut layers are stacked, aligned and bonded.
- Production-Ready Tooling: Once post-processed, the assembled layers create durable, full-scale tooling ready for use in prodution, with minimal material waste and high-dimensional accuracy.
Key Features
- The process reduces material waste compared to traditional block machining.
- It allows large tools to be made without oversized equipment
- Material versatility means you can choose the best substrate for your application.
Designed for tooling, pattern and mold makers in foundry, marine and industrial manufacturing. Ideal fo rindustries looking to speed production, reduce waste and expand material options.
Why It Matters
- Faster Turnaround: From CAD file to finished tool in days.
- Material Flexibility: Composites, metals, wood and plastics.
- Cost and Waste Reduction: Less material waste than block machining.
- Scalable Production: Large tooling without oversized equipment.
Designed for tooling, pattern and mold makers in foundry, marine and industrial manufacturing. Ideal fo rindustries looking to speed production, reduce waste and expand material options.
Thermwood's CutLayer Machine
- Designed specifically for CutLayer manufacturing
- The machine KNOWS how to make a CutLayer part from a simple CAD model
- Automatically creates the nested CNC program needed to machine each layer in segments
- Adjusts layer-segment geometry to provide a specified trim stock
- Prints information on each segment telling you what layer it’s on
- Prints identifier on each segment telling you its position on that layer and what it connects to
- Prints a QR code on each part making it easy to re-machine a part, if ever needed
- Machines joints between layer-segments to connect them, to make full layers
- Drills dowel alignment holes to provide precise layer to layer alignment
- Prints dowel insertion markers on each part to further simplify assembly
- Staggers segment joints for a more solid structure
- Drills and taps attachment holes between two or more layers so that metal layers can be bolted together
- Machines internal passages for internal heating or cooling fluid (coming)
- Internal “Anchor Points” facilitate adding internal stiffening structure (coming)
- Tab construction keeps parts from moving during machining
- Automatic tool changer with up to 12 tools
- 13 HP, 24,000 RPM router head for fast machining
- 5’x12’ vacuum cutting table
Aerospace Layup Tool
Aerospace layup tool is made form epoxy-fused fiberboard with plural component urethane coating. it was made using about $2,000 worth of material in less time than it took to additively print the same part.
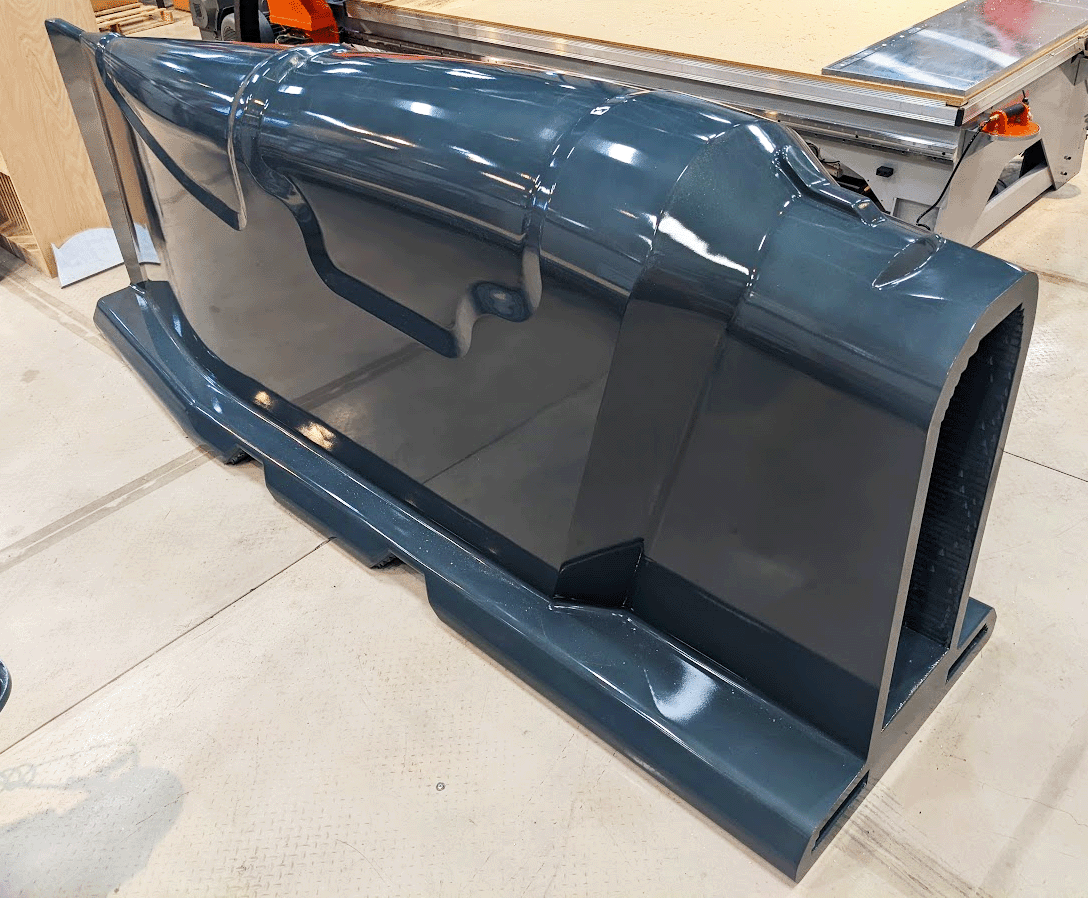
Aluminum Trim Fixture
Aluminum aerospace trim fixture made using cut layer additive process. Although it looks solid, the surfaces are all only about an inch thick, which means it uses a minimum amount of material.
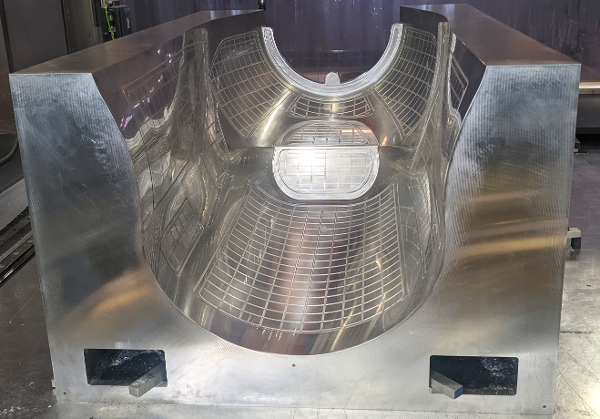

Aluminum Thermoforming Mold
This is a CutLayer Thermoforming mold made of aluminum. It includes 3 vacuum chambers and 6 liquid channels, end to end, used to control mold temperature, all machined completely inside the 2” thick mold face.

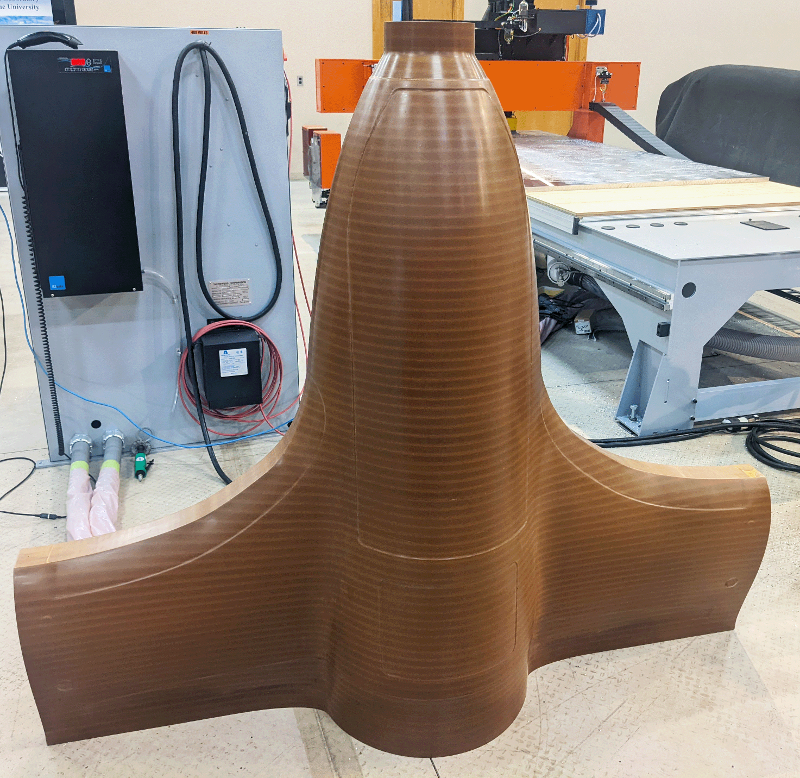
Drone Pattern
One of the first parts made using cut layer additive and less than $400 worth of material.
CutLayer Machine
Cut Layer Additive Machine with Advanced machine Intelligence, built specifically for the Cut Layer Additive process, costs considerably less than other large format near net shape additive systems.

Machine Intelligence
Machine intelligence means you show the machine what you want using a simple interactive process that requires a tiny fraction of the time it would normally take using traditional programming.
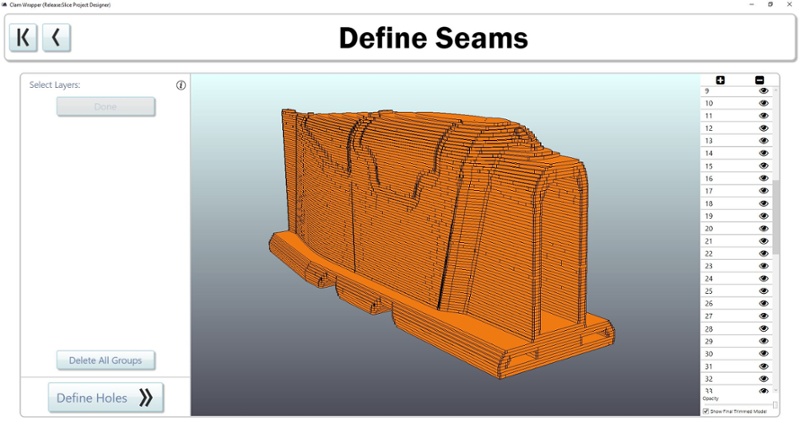
Efficient Nesting
Breaking layers into segments means highly efficient nesting. Unique joinery makes putting layers back together really easy.
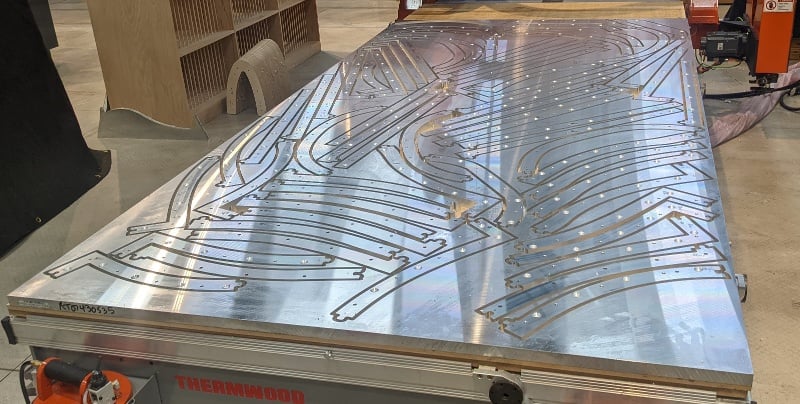

Easy Assembly
Machine printing tells you which layer the part is on, its position on the layer and where dowels need to be inserted, making assembly easy. QR code makes re-cutting the part easy, if you ever need to.




